NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems Ex 1.3
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 1.
Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has :(1)
(2)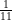
(3) 4
(4)
(5)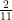
(6)
Solution:
(1) = 0.36, terminating.
= 0.36, terminating.
(2) By long division, we have

(3)


Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has :(1)
(2)
(3) 4
(4)
(5)
(6)
Solution:
(1)
(2) By long division, we have

(3)


∴ 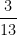 = 0.23076923 =
= 0.23076923 = 
(5)

∴ = 0.181818 =
= 0.181818 = 
(5)

∴
(6)


Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 2.
You know that =
=  .Can you predict what the decimal expansions of
.Can you predict what the decimal expansions of 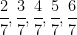 are, without actually doing the long division? If so, how? [Hint: Study the remainders while finding the value of
are, without actually doing the long division? If so, how? [Hint: Study the remainders while finding the value of  carefully.]
carefully.]
Solution:
We have, =
= 

You know that
Solution:
We have,

Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 3.
Express the following in the form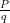 , where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
Express the following in the form
- 0.
Solution:
(1) Let x = = 0.666………… …(i)
= 0.666………… …(i)
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 10, we get
10x = 6.666… …(ii)
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (ii), we get
(10x – x) = (6.666…) – (0.666…)
9x = 6 => x = 6/9 => x = 2/3
x = 0. = 0.4777
= 0.4777
(1) Let x =
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 10, we get
10x = 6.666… …(ii)
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (ii), we get
(10x – x) = (6.666…) – (0.666…)
9x = 6 => x = 6/9 => x = 2/3
x = 0.
(2) Let
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 10, we get
10x = 4.777… …(ii)
Multiplying Eq. (ii) by 10, we get
100x = 47.777 … (iii)
On subtracting Eq. (ii) from Eq. (iii), we get
(100x-10x)= (47.777…) – (4.777…)
90x =43 => x =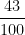
x =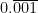 = 0.001001001…
= 0.001001001…
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 10, we get
10x = 4.777… …(ii)
Multiplying Eq. (ii) by 10, we get
100x = 47.777 … (iii)
On subtracting Eq. (ii) from Eq. (iii), we get
(100x-10x)= (47.777…) – (4.777…)
90x =43 => x =
x =
(3) Let
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 1000, we get
1000x = 1.001001001…
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (ii), we get
(1000x – x) = (1.001001001…) – (0.001001001…)
999x = 1 =>
Multiplying Eq. (i) by 1000, we get
1000x = 1.001001001…
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (ii), we get
(1000x – x) = (1.001001001…) – (0.001001001…)
999x = 1 =>
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 4.
Express 0.99999… in the form . Are you surprised by your answer? With your teacher and classmates discuss why the answer makes sense.
. Are you surprised by your answer? With your teacher and classmates discuss why the answer makes sense.
Solution:
Let x = 0.9999… …(i)
Here, we have only one repeating digit. So, we multiply both sides of (i) by 10 to get
Express 0.99999… in the form
Solution:
Let x = 0.9999… …(i)
Here, we have only one repeating digit. So, we multiply both sides of (i) by 10 to get
10x = 9.999…. …(ii)
Subtracting (i) from,(ii), we get
10x-x = (9.999…)-(0.9999…)
=> 9x = 9
=> x = 1
Hence, 0.9999…= 1
Since, 0.9999… goes on forever. So, there is no gap between 1 and 0.9999… and hence they are equal.
Subtracting (i) from,(ii), we get
10x-x = (9.999…)-(0.9999…)
=> 9x = 9
=> x = 1
Hence, 0.9999…= 1
Since, 0.9999… goes on forever. So, there is no gap between 1 and 0.9999… and hence they are equal.
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 5.
What can the maximum number of digits be in the repeating block of digits in the decimal expansion ? Perform the division to check your answer.
? Perform the division to check your answer.
Solution:

What can the maximum number of digits be in the repeating block of digits in the decimal expansion
Solution:

Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 6.
Look at several examples of rational numbers in the form (q ≠ 0), where, p and q are integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations (expansions). Can you guess what property q must satisfy?
(q ≠ 0), where, p and q are integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations (expansions). Can you guess what property q must satisfy?
Solution:
Consider many rational numbers in the form (q ≠ 0) , where p and q are
(q ≠ 0) , where p and q are
integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations.



From the above, we find that the decimal expansion of the above numbers is terminating. Along with we see that the denominator of the above numbers are in the form 2m x 5n, where m and n are natural numbers. So, the decimal representation of rational numbers can be represented as a terminating decimal.
Look at several examples of rational numbers in the form
Solution:
Consider many rational numbers in the form
integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations.

From the above, we find that the decimal expansion of the above numbers is terminating. Along with we see that the denominator of the above numbers are in the form 2m x 5n, where m and n are natural numbers. So, the decimal representation of rational numbers can be represented as a terminating decimal.
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 7.
Write three numbers whose decimal expansions are non-terminating non-recurring.
Solution:
Three numbers whose decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating are
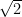 ,
, and
and 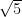 or we can say 0.100100010001…, 0.20200200020002… and 0.003000300003…
or we can say 0.100100010001…, 0.20200200020002… and 0.003000300003…
Write three numbers whose decimal expansions are non-terminating non-recurring.
Solution:
Three numbers whose decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating are
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 8.
Find three different irrational numbers between the rational numbers and
and  .
.
Solution:
To find irrational numbers, firstly we shall divide 5 by 7 and 9 by 11,

Thus, = 0.8181… =
= 0.8181… = 
The required numbers are
0.73073007300073000073…
0.7650765007650007650000…
0.80800800080000…
Find three different irrational numbers between the rational numbers
Solution:
To find irrational numbers, firstly we shall divide 5 by 7 and 9 by 11,

Thus,
The required numbers are
0.73073007300073000073…
0.7650765007650007650000…
0.80800800080000…
Ex 1.3 Class 9 Maths Question 9.
Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational:
(1)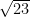
(2)
(3) 0.3796
(4) 478478…
(5) 1.101001000100001…
Solution:
(1)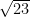 is an irrational number as 23 is not a perfect square.
is an irrational number as 23 is not a perfect square.
(2)


Thus, 15 is a rational number.
(3) 0.3796 is a rational number as it is terminating decimal.
(4) 7.478478… is non-terminating but repeating, so, it is a rational number.
(5) 1.101001000100001… is non-terminating and non-repeating so, it is an irrational number.
Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational:
(1)
(2)
(3) 0.3796
(4) 478478…
(5) 1.101001000100001…
Solution:
(1)
(2)

Thus, 15 is a rational number.
(3) 0.3796 is a rational number as it is terminating decimal.
(4) 7.478478… is non-terminating but repeating, so, it is a rational number.
(5) 1.101001000100001… is non-terminating and non-repeating so, it is an irrational number.
Thus, =
= 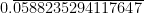
∴ The maximum number of digits in the quotient while computing are 16.
are 16.
∴ The maximum number of digits in the quotient while computing








0 comments:
Post a Comment
THANK YOU